When the electrical signals that control heartbeat are delayed or totally blocked, the condition is known as heart block. This may result in irregular heartbeats causing symptoms such as exhaustion, weakness, palpitations, fainting or, in extreme cases, major cardiac problems.
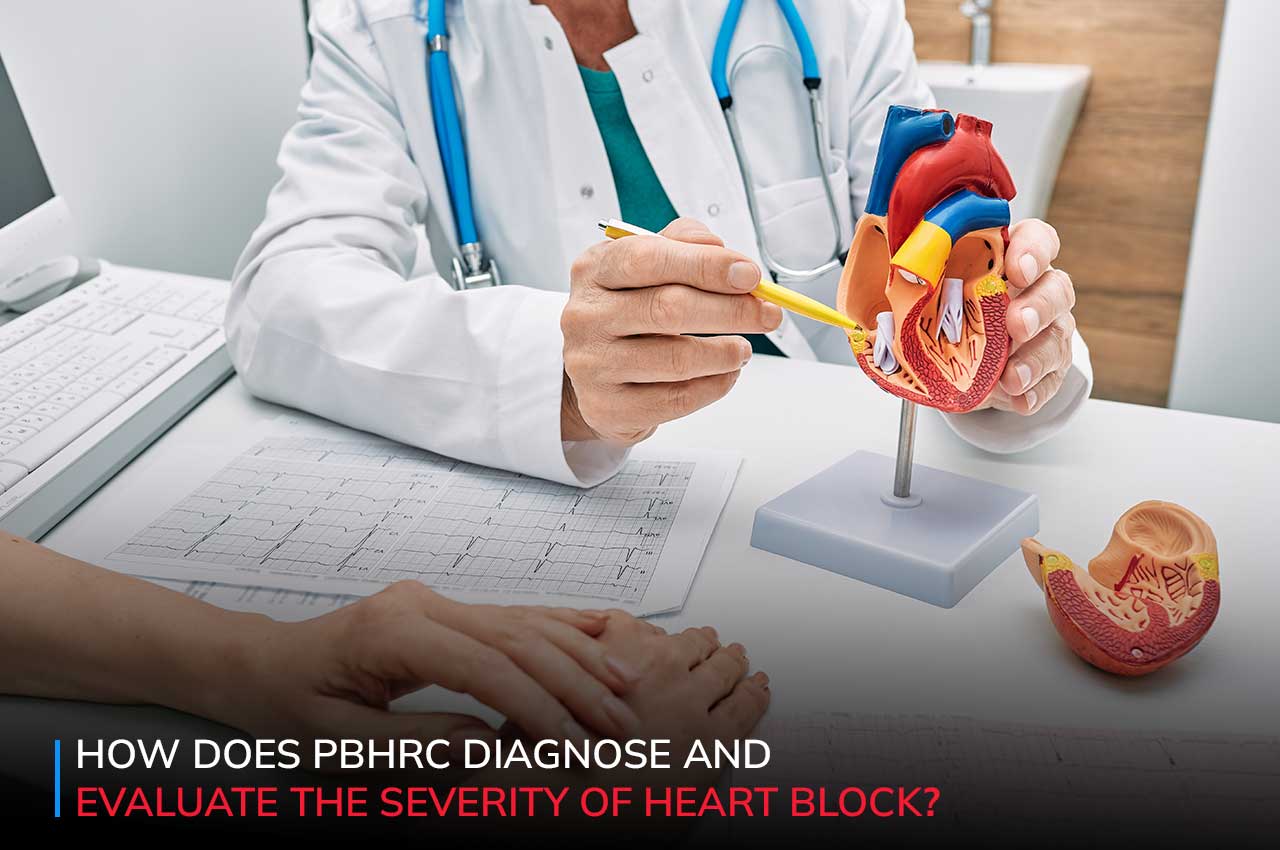
In order to stop additional heart damage, early diagnosis and treatment are crucial. The type and severity of heart block are determined at the P Banerji Homoeopathic Research Clinic (PBHRC) by patient evaluation, several pieces of diagnostic equipment and customised treatment plans.
A disturbance in the electrical conduction system of the heart is the primary cause of the heart block. It is essential to understand the causes of heart block since the right treatment and long-term care can be determined by the underlying causes.
Since focused intervention can stop conditions from getting even worse, determining the exact cause of heart block is essential. The underlying causes of heart block can be found through patient evaluation and diagnostic procedures like echocardiography and ECG.
Based on the location and degree of the conduction delay, heart blocks are divided into four categories. Understanding the type is crucial because it dictates the line of treatment to be adopted.
The least severe form of conduction disturbance is referred to as first-degree heart block, where electrical signals are delayed but still get to the ventricles. Many patients suffering from this type of heart block are asymptomatic or experience fatigue or palpitations.
Second-degree heart block falls into two types: Mobitz Type I (Wenckebach) and Mobitz Type II. In Mobitz I, the PR interval lengthens, and the next electrical signal is lost, skipping a beat and causing dizziness and palpitations. Mobitz Type II also involves intermittent blocking of electrical signals getting to ventricles, which could lead to complete heart block and cause fainting, fatigue or shortness of breath. The sooner a heart block is detected, the underlying causes of heart block can be identified and treated.
A third-degree heart block, or complete heart block, occurs when no electrical impulses are transmitted from the atria to the ventricles. The ventricles produce a slower rhythm, which may be inadequate to meet the needs of the rest of the body. Patients frequently describe severe dizziness, fainting, fatigue, and the extreme possibility of sudden cardiac arrest. This type requires immediate medical assessment and appropriate treatment for heart block.
A bundle branch block occurs when the electrical impulse is blocked in one of the bundle branches of the heart. Some patients remain asymptomatic, while others experience palpitations or shortness of breath. A bundle branch block often suggests heart disease and is something that needs to be taken into account both in an assessment of the causes of heart block and in planning treatment for heart block.
At PBHRC, we offer homoeopathic treatment as an adjunct to traditional measures. Our homoeopathic treatment focuses on the holistic well-being of the patient and support for heart function. The homoeopathic remedies are then determined based on patient symptoms, constitution, and the type of heart block. Homoeopathic remedies can help improve blood flow, support heart health, reduce palpitations, and alleviate related symptoms like tiredness or dizziness.
Sources